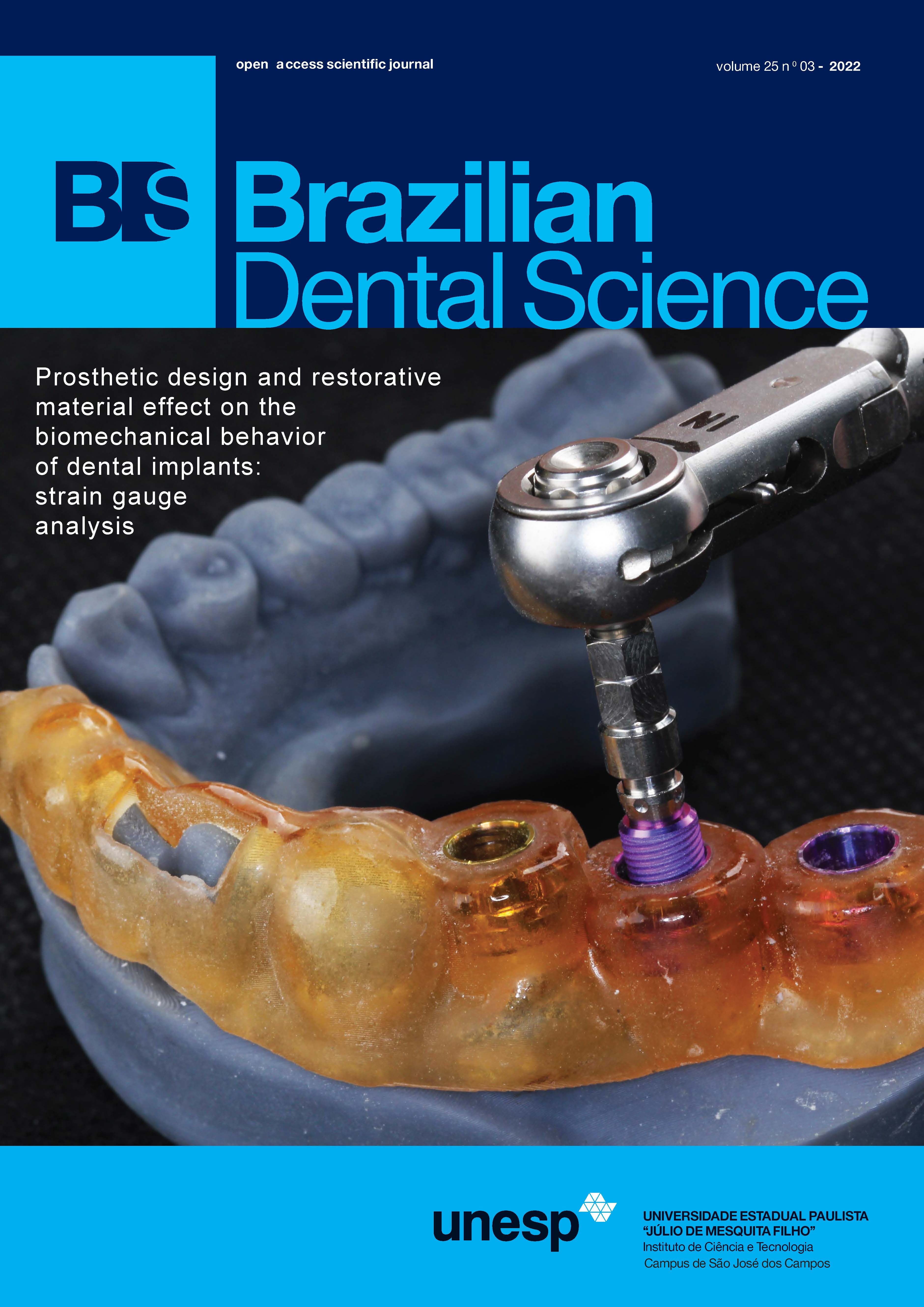
Assessment of sCD14 levels in patients with endodontic pathology requiring root canal treatment
sCD14 levels in patients with endodontic pathology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4322/bds.2022.e2809Abstract
Objective: Dental caries is one of the most common microbial diseases. Because of the infectious nature
of the disease, the immunologic response by the host plays an essential role in its development. Therefore,
the aim of this study was to evaluate the sCD14 levels in patients exhibiting two to three teeth with caries
involving pulp along with apical periodontitis requiring root canal treatment. Material and Methods: This
study was carried out on 20 participants, of whom 10 were caries-free (Control) and 10 had two to three
teeth with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis along with apical periodontitis requiring root canal treatment,
within the ages of 20- 30 years. Unstimulated saliva of the participants was collected with disposable needleless
syringe from buccal and labial vestibules. The sCD14 levels in salivary samples were assessed before and
following endodontic treatment. The results were analyzed by ELISA. Results: The obtained levels of sCD14
were analyzed statistically. Paired T test was performed to assess the significance. The results revealed that
there was a significant difference in sCD14 levels with a P=0.0005, as it had drastically reduced once the
inflammation has subsided. Conclusion: Higher values of sCD14 levels were seen in patients with symptomatic
irreversible pulpitis along with apical periodontitis than in caries free group. The study also showed that sCD
levels were significantly reduced following post endodontic treatment. Therefore, increased levels of sCD14
can be considered as a marker of inflammation.
KEYWORDS
Dental caries; Apical periodontitis; Dental caries; ELISA; sCD14.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Versions
- 2022-07-12 (2)
- 2022-07-12 (1)
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Brazilian Dental Science uses the Creative Commons (CC-BY 4.0) license, thus preserving the integrity of articles in an open access environment. The journal allows the author to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
=================